Competitive Advantages
Baanto’s ShadowSense technology tackles the limitations of traditional touchscreens head-on. It excels where others fail—working flawlessly in bright light, with gloved hands, and in rugged environments. By eliminating false touches and offering precise, reliable input, ShadowSense delivers the durability and performance industries need for mission-critical applications.
ShadowSense vs Capacitive Touch
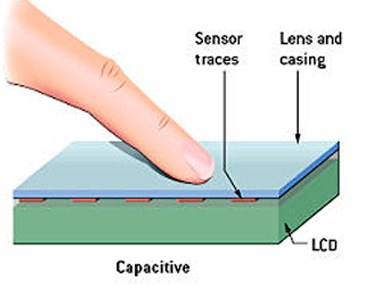
Capacitive touch screens are made of single or multiple layers of material that are coated with a conductor such as Indium Tin Oxide. A protective cover seals the assembly off from the environment.
When another electrical conductor, like a bare fingertip or a stylus, touches the surface, an electric circuit is completed at that location. Sensors embedded in the glass then detect the location of the flow of current, which is then registered as a touch event.
This is different from the way that resistive touch technology works, where physical pressure is involved.
Pros of Capacitive Touch Screens
- Can support multi touch gestures like flick, pinch and swipe
- Are durable and robust; up to a point
- Last longer because there are no moving parts
- Are sensitive and even a light touch can register an input
- Are highly responsive
Capacitive touch technology can be divided into:
Surface Capacitive
This is a simpler form of capacitive touch screen, with only one side of the insulator coated with transparent conducting material and electrodes placed at the four corners of the screen. When a conductor touches the screen, different quantities of current will flow from the electrodes to the conductor. The location can be calculated based on the ratio of these currents.
Projected Capacitive
A projected capacitive touch (PCT) screen is a solid state device that has two types of electrodes, called X and Y electrodes, in separate layers running in mutually perpendicular directions. When the conductor touches the screen, the electrical field between the X and Y electrodes change and sensors can instantly pinpoint the location.
The Baanto ShadowSense Advantage
If you have ever tried to use the touch screen of your phone when it is wet, or when wearing gloves, you will know the limitations of capacitive screens. Apart from being unable to perform in such situations, capacitive touch screens also have other issues.
Baanto ShadowSense touch screens are designed to overcome these issues.
Cons of Capacitive Touch Screens | ShadowSense Benefits |
| Might not be able to work with non conductors of electricity like gloved fingers | Screens work with non conductors like gloved fingers or paintbrushes |
| Affected by high humidity, dust and viscous fluids as they interfere with conductivity | Screens work even when covered with water, ketchup, grease or foreign objects like mud |
| Affected by “ghosting” due to build up of static electricity, causing the screen to lock up or malfunction | The screen will not “ghost” |
| Are costly to fabricate because of two ITO screens, and do not scale economically | Screens can scale up cost effectively to sizes of 267’’ without any compromise in performance |
| May be affected by electrical noise and susceptible to scratches | Screens cannot be scratched, even by a coin or a credit card and is not affected by electrical interference |
| Will not work if the screen is cut or smashed as the ITO layer will be affected | Touch function is independent of the glass and screen will keep on working even if it is broken |
ShadowSense vs Resistive Touch
The next time you are using a touch screen ATM, simply touch the screen without applying any pressure. You will find that the machine will not accept any input.
Apply pressure on the screen and it will start working. This is resistive touch technology in action.
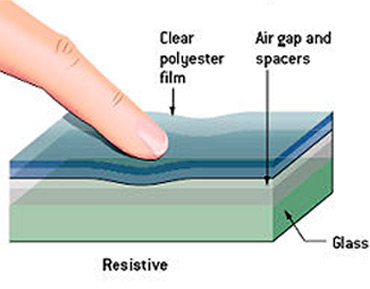
A resistive touch screen is made of two transparent layers of glass or plastic, each coated with a conducting layer of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO). The conducting sides face one another and are separated by an air gap.
When pressure is applied by the user, the top layer bends and touches the bottom layer. This causes a small amount of current to flow at the point where they connect. The location of the touch event can then be measured by the sensors.
Unlike most other types of touch screens (capacitive, infrared touch screen technology ) these screens have moving parts.
Pros of Resistive Touch Screens
- Inexpensive to make
- Can accept an input from anything, including pens, gloved fingers etc
- Can be easily assembled from the component parts; screens and sensors
- Can work in rain or in the presence of other fluids
Resistive touch technology can be divided into:
Analog 4 wire resistive
In this variant, if the top sheet has electrodes for the vertical direction (Y), the bottom sheet will have electrodes for the horizontal direction (X). The top and bottom sheets measure each others’ voltages and based on that sensors can determine the location of the touch point.
Analog 5 wire resistive
In this variant, the voltage of the bottom sheet is measured by the top sheet, with electrodes placed at four corners of the bottom sheet. The top sheet does not have any electrodes.
Analog 8 wire resistive
These screens are similar to Analog 4 wire screens. The only difference is an extra set of electrodes, which automatically take care of alignment and recalibration issues that crop up in the 4 wire screens over long term use.
The Baanto ShadowSense Advantage
Resistive touch screens have a number of issues which are addressed by ShadowSense touch screens.
Cons of Resistive Touch Screens | ShadowSense Benefits |
| Poor limited touch accuracy based on number of ‘wires’ | High precision 4K resolution based on the ADC resolution of the sensors, not limited by screen size or topology |
| Limited to 1-2 touches and has difficulty processing gestures | True multi-touch performance with capability to discern complex multi-touch gestures |
| High activation force is required | Zero activation force, will work with soft gloved fingers, styluses, passive objects |
| Resistive layers are mechanical in nature and tend to wear out quickly | No wear from touch, completely reliant on light and shadows. No moving parts and > 200,000 MTBF for critical long-term operations |
| Very limited optical transmissions due to resistive layers on top of LCD | No layers over the display glass, Maintains 100% of display clarity and brightness |
| Performs poorly in harsh, outdoor, or industrial environments | Excellent performance with no degradation in harsh environments. |
ShadowSense vs Infrared Touch
Even as ShadowSense operates using Infrared light, the technology is fundamentally different than standard ‘IR touch screens’.
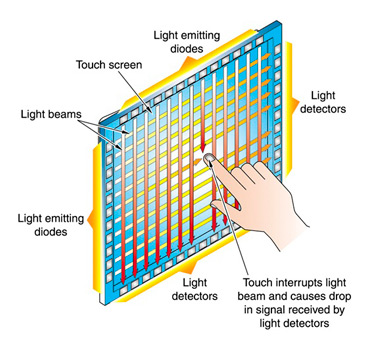
Infrared touch screens operate by calculating light-beam interruption, or “beam break”, to determine the location of touch events. This is a perimeter-based touch technology differing from Surface Acoustic Wave, in that infrared light beams are used and not ultrasonic waves.
Using LEDs and light sensors placed on the vertical and horizontal axis of a bezel, the Infrared system casts a grid of light across the screen. When an object touches the screen, it interrupts the light beams on the grid causing the light to be blocked from the sensor. This loss of light is used to determine the location of the touch. Since the LEDs and sensors make a grid, the touch results in an X and Y coordinate from the beam break. These coordinates then communicate with the display to react with the software on screen.
Pros of Infrared Touch Screens
- Inexpensive to make
- Can accept an input from anything, including pens, gloved fingers etc
- Can be easily assembled from the component parts; screens and sensors
The Baanto ShadowSense Advantage
Resistive touch screens have a number of issues which are addressed by ShadowSense touch screens.
Cons of Infrared Touch Screens | ShadowSense Benefits |
| Poor limited touch accuracy based on number of ‘LED beams’ | High precision 4K resolution based on the ADC resolution of the sensors, not limited by screen size or topology |
| Generally poor multi-touch performance | True multi-touch performance with capability to discern complex multi-touch gestures |
| Lack of size and shape determination | Can detect size and shape of object, differentiate between fingers, stylus, eraser and large objects such as palm |
| Very poor sunlight immunity | Completely impervious to sunlight and any ambient light |
| Prone to false inputs from dust, debris and requires calibration | Excellent filters capable of rejecting false touches and constantly self calibrates |
| Performs poorly in harsh, outdoor, or industrial environments | Excellent performance with no degradation in harsh environments. |